

PAVLOV THEORY TRIAL
Advantages and Disadvantages of Solving a Problem Through Trial and Error.Trial and Error Theory of Learning and Its Educational Implications.Thorndike Multifactor Theory of Intelligence.Discuss the Relationship Between the Teacher and the Learner.Social Constructivist Learning Theory in the Classroom.Assumptions and Beliefs about Teaching and Learning in Education.Different Approaches to Teaching and Learning in Education.Advantages and Disadvantages of Humanistic Learning Theory.Humanism Learning Theory and Implementation in the Classroom.Implications of Humanistic Theory in Teaching and Learning.Characteristics of Humanistic Approach to Learning in the Classroom.Role of Teacher as a Co Learner in Different Teaching Learning Situation.Role of Teacher as a Negotiator in Teaching and Learning Process.Role of Teacher as a Transmitter of Knowledge B.Ed Notes.Role of Teacher as a Facilitator in Assessment for Learning.

Explain Information Processing Theory of Learning with Example.Concept of Learning According to Cognitive Information Processing Theory.Application of Behaviorism Learning Theory in Classroom Setting.Role of a Teacher in Behaviouristic Approach to Education.Characteristics of Behaviorist Theory of Language Acquisition.The first psychologists who applied classical conditioning’s principles to human behavior were Watson and Rayner to learn more about the development of different phobias. The bell became the conditioned stimulus and the salivation became the conditioned response.

He started feeding the dogs with the sound of a bell repeatedly and after some repetitions, the fig started salivating every time they heard the sound of a bell. Following this, he gave them food (unconditioned stimulus) and they salivated (unconditioned response). Each time the dog heard the bell ring, the dog was fed due to which it started associating the sound of the bell with the image of food.įirstly, he produced a sound of a bell to which the dog did not respond, which was a neutral response.
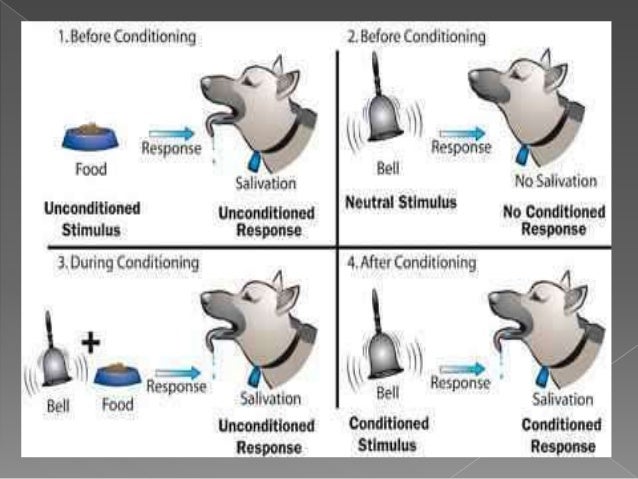
Pavlov conducted his experiments mostly on dogs who were known to salivate as a response to a bell. In this stage, the conditioned stimulus is associates with the unconditioned stimulus to produce a new conditioned response. This stage involves a stimulus that produces neutral or no response and is associated with an unconditioned stimulus which then becomes a conditioned stimulus. The organism produces an unlearned response. This stage involves a natural response or an unconditioned response of an organism produced by an unconditioned stimulus. There are three stages of classical conditioning which are as follows: Before Conditioning (Stage 1) The process involves two stimuli that are linked to arouse a response from a person or an animal which is learned. Ivan Pavlov was a Russian psychologist who discovered the classical conditioning theory which means learning through association.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
